How Long Can a Catfish Live Out of Water? (Quick Read)

Have you ever wondered How Long Can a Catfish Live Out of Water? Catfish are fascinating creatures, with their sleek bodies and distinctive whisker-like barbels. In this article, we will delve into the intriguing world of catfish behavior, exploring their unique adaptations for survival, debunking common myths, and understanding the factors that influence their ability to thrive in both aquatic and terrestrial environments.
How do Fish Breathe in Water?
Exploring the underwater respiration process in fish unveils a captivating journey. Let’s delve into a detailed explanation:
Oxygen in water: Unlike the air, water holds notably less oxygen. However, in clean and well-aerated water, the dissolved oxygen is ample for the survival of fish.
Gills: Fish primarily respire through their gills, which are situated on both sides of their heads and safeguarded by a flap. These intricate organs boast feathery structures, each filament teeming with tiny blood vessels. This design amplifies the surface area, facilitating efficient gas exchange.
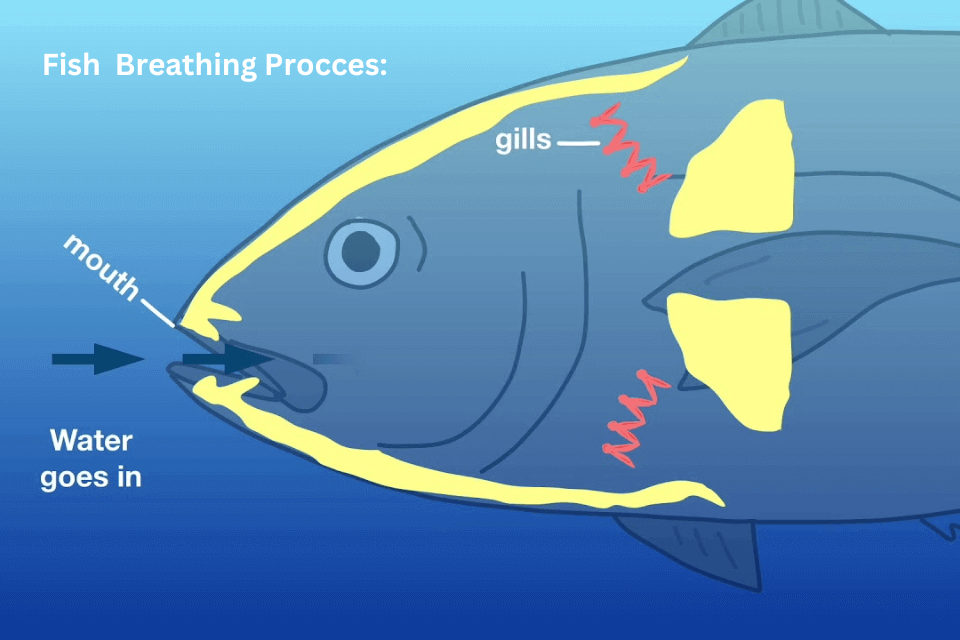
In the respiration process:
- Water Intake: Fish open their mouths to intake water.
- Water Flow: The water subsequently flows over the filaments in the gills.
- Oxygen Absorption: Dissolved oxygen in the water diffuses into the blood vessels within the filaments.
- Carbon Dioxide Release: Carbon dioxide, a result of cellular respiration, undergoes diffusion from the blood vessels into the water.
- Water Expulsion: Deoxygenated water is then expelled through the gill covers.
Efficiency and adaptations: Gills exhibit remarkable efficiency in extracting oxygen from water, yet various fish species tailor their gills to suit specific needs and environments. Certain fish boast larger gills, enhancing their capacity to extract oxygen in low-oxygen surroundings. In contrast, others feature specialized gill structures designed to filter out substances like sand or mud, reflecting their adaptation to particular environmental conditions.
Beyond gills: Certain fish, like lungfish and catfish, have developed additional adaptations for breathing air. They can either gulp air directly from the surface or employ specialized organs to extract oxygen from the water.
Factors affecting fish breathing: The efficiency of fish breathing can be influenced by factors such as water temperature, oxygen levels, and pollution. In warmer water, oxygen content tends to decrease, while pollution can obstruct the gills, hindering the uptake of oxygen.
How Long Can a Catfish Live Out of Water?

Removing a catfish from water often results in its demise within an hour, but there are occasional instances of survival lasting up to 18 hours, though such occurrences are uncommon. If your catfish manages to persist for a few hours under these conditions, it can be deemed a noteworthy success. This variability in survival times emphasizes the unique adaptability of catfish and underscores the importance of understanding their resilience when exposed to environments outside their aquatic habitats. Let’s dive into more details.
As mentioned earlier, certain catfish have demonstrated an impressive ability to survive for 18 hours after being removed from their natural aquatic habitat.
The typical lifespan of a catfish outside of water is usually a few hours, seldom exceeding three. Surprisingly, this relatively short duration is considered quite a substantial period in these circumstances.
In general, most fish succumb within a mere 10 minutes when removed from water. Some perish even more swiftly, while others manage to endure for days, relying on oxygen absorption through their skin.
I’ll delve deeper into the reasons behind fish mortality outside of water in the upcoming sections.
Now, what enables a catfish to endure for an extended period, and what factors influence a fish’s ability to stay alive for a few hours?
Catfish are recognized for their capacity to thrive in environments with low oxygen levels and demonstrate resilience in such conditions.
Trout, residing in pristine, well-aerated waters, are prone to swift demise within minutes when removed from their habitat.
Fish with a sluggish metabolism, found in frigid waters, exhibit prolonged survival capabilities as their oxygen requirements diminish. An illustrative example is the pike caught during ice fishing, showcasing their ability to endure extended periods in such cold conditions.
In warmer months, the same fish faces a quicker demise as heightened metabolism, and active feeding contribute to a faster rate of mortality.
I brought up various species to illustrate why a duration of a few hours is considered noteworthy and to highlight the factors influencing it.
The duration catfish can endure outside water and their survivability are influenced by external factors like sun exposure, air temperature, and humidity. Naturally, one shouldn’t anticipate prolonged survival on a hot, dry, sunny day without any cover.
Interesting Fact About Walking Catfish
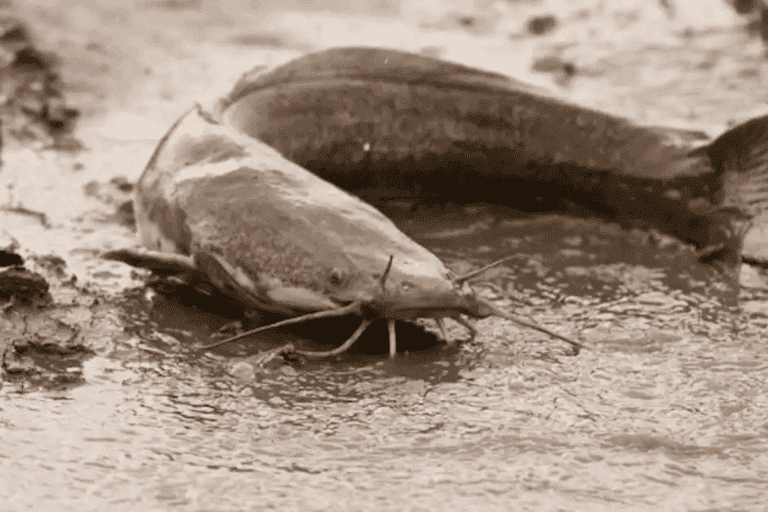

Meet the walking catfish, a remarkable species known for its unique adaptation to terrestrial life. Thriving in hypoxic and muddy waters, this catfish showcases an extraordinary ability to navigate dry land. Using its pectoral fins, it wiggles from one pond to another when its habitat dries out. Notably, the walking catfish can absorb oxygen through its skin, allowing it to survive for hours outside water. While this terrestrial excursion has its limits, it sheds light on the catfish’s resilience and ingenuity in adapting to challenging environmental conditions. An intriguing glimpse into the extraordinary world of the walking catfish.
Catfish Conservation
Catfish conservation stands as a critical endeavor, addressing the preservation of diverse catfish species and their ecosystems. Threatened by habitat loss, pollution, and overfishing, these aquatic marvels require concerted efforts to ensure their continued existence. Conservation initiatives involve habitat restoration, sustainable fishing practices, and public awareness campaigns. By safeguarding their habitats, promoting responsible fishing, and educating communities, catfish conservation strives to maintain biodiversity and ecological balance. Recognizing the pivotal role catfish play in aquatic ecosystems, these efforts contribute to the overall health of water environments, fostering a sustainable coexistence between these fascinating creatures and their ecosystems.
What are the methods to keep catfish alive after catching them?
Maintaining the health and vitality of catfish is paramount when practicing catch-and-release. It’s essential to ensure that the fish remains unharmed during the process.
Minimize the duration the fish spends out of the water as much as possible. Take only the necessary time to safely unhook the fish and capture a photo. Ensure that the hook removal process is gentle to avoid any harm to the fish, and opt for hooks specifically designed for this purpose.
Begin by using a net to safely lift the fish out of the water and place it on an unhooking mat. Once the hook is removed, handle the fish with care if you wish to take a photograph before releasing it back into the water. Avoid rough handling and refrain from tossing the fish back into the water.
Sometimes, anglers find themselves in situations where they must temporarily keep the fish alive and are unable to release it immediately.
Should you need to keep the catfish for an extended duration, consider investing in a quality and roomy live well. Some models come equipped with aerators to ensure an ample supply of oxygen. Keep a close watch on the water temperature, preventing it from rising excessively when using aerators. Regularly clean the live well after each use to maintain the catfish’s well-being, ensuring it survives and stays in good health for a safe release.
If needed, gradually incorporate a small amount of ice into the live well to lower the temperature. Ensure the cooling process is gradual and doesn’t drop the temperature too significantly. A sudden temperature decrease can be shocking for the fish. Likewise, when releasing it into warmer water again, be cautious, as subjecting the fish to a sudden change in temperature can induce a similar shock.
Interesting Catfish Facts
Catfish, with their diverse species, harbor intriguing facts that unveil their unique characteristics. Renowned for their exceptional adaptability, some catfish possess the ability to survive out of water for extended periods. Walking catfish, a notable variety, can navigate on land by wiggling with their pectoral fins. Their resilience thrives in hypoxic waters, showcasing their extraordinary survival skills. Interestingly, catfish are known for their distinctive barbels, sensory organs resembling whiskers, aiding in navigation and locating prey. Some species, like the flathead catfish, display impressive sizes, with individuals exceeding 100 pounds. These captivating facts underscore the diversity and resilience of this fascinating aquatic species.
What Causes a Catfish to Die When Taken Out of Water

Now that you’re aware of how long can a catfish live out of water and ways to enhance its lifespan, consider…
What Causes a Catfish to Die When Taken Out of Water?
Fish, including catfish, rely on their gills to extract oxygen from water, their primary breathing method. Although some fish can absorb oxygen through their skin, gills serve as their primary respiratory organs. Due to their anatomical and biological structure, fish cannot extract atmospheric oxygen from the air using their gills. When taken out of water, fish undergo suffocation, leading to their eventual demise.
Similar challenges arise for mammals underwater, as their respiratory systems are adapted for breathing air.
Fish species that can absorb some oxygen through their skin face mortality when removed from water, albeit with an extended survival period. Evolving for life underwater, fish lack the protective layers of land animals, possess eyes unsuited to terrestrial life, and experience considerable damage to their delicate gills when not submerged. Even if the fish doesn’t suffocate immediately, its survival is compromised, leading to inevitable death.
Fish can experience suffocation even in water, especially if the water lacks sufficient oxygen. In contrast, catfish can endure extremely low oxygen levels but still require some for survival. Certain fish species, like the African sharp-toothed catfish, showcase remarkable adaptations. They can survive in mud puddles, awaiting rain and water, thanks to specific evolutionary adjustments and additional organs. This adaptation allows them to endure challenging conditions until suitable aquatic environments are reestablished.
Conclusion
In exploring the How Long Can a Catfish Live Out of Water, we’ve uncovered the captivating realm of their behavior, resilience, and survival instincts. From the unique adaptations of the walking catfish to the critical importance of catfish conservation, these aquatic wonders offer a glimpse into a world of diversity and adaptability. Understanding how long a catfish can live out of water sheds light on their remarkable survival strategies, emphasizing the delicate balance between aquatic and terrestrial environments. As we navigate through the methods of keeping catfish alive after catching them and the fascinating facts about these creatures, we gain a richer appreciation for the interconnectedness of their existence.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Q: Can all catfish survive out of water for some time?
A: While catfish have unique adaptations for survival, not all species can endure extended periods out of water. The ability varies among different catfish species.
- Q: What should I do if my pet catfish shows signs of distress?
A: Immediate actions include checking water quality, adjusting conditions, and consulting with a veterinarian if necessary. Recognizing behavioral indicators is crucial for timely intervention.
- Q: Are there any endangered catfish species?
A: Yes, several catfish species face the threat of extinction due to habitat destruction, pollution, and overfishing. Conservation efforts are underway to protect these endangered species.
- Q: Can catfish live in both saltwater and freshwater environments?
A: Most catfish species are freshwater inhabitants, but some are adapted to brackish water. Only a few catfish species can tolerate saltwater environments.
- Q: How long do walking catfish survive on land?
A: Contrary to the term “walking catfish,” they don’t truly walk on land. They exhibit unique movements, but their survival time out of water is limited, typically a matter of hours.





